How Long Does a Cigarette Burn? Unveiling the Factors and Implications
The question of how long does a cigarette burns for seems simple, but the answer is surprisingly complex. It’s not a fixed number; instead, it’s influenced by a multitude of factors, from the type of tobacco used to the smoker’s puffing habits and even environmental conditions. Understanding these variables not only satisfies a common curiosity but also provides insights into smoking behavior, nicotine delivery, and the potential health consequences. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the science and practical considerations surrounding cigarette burn times, offering a level of detail and expertise unmatched by other resources.
We’ll explore the typical burn time, dissect the factors that cause variations, and discuss the implications for smokers and those around them. Whether you’re a smoker seeking to understand your habit better or simply curious about the world around you, this article will provide a thorough and informative exploration of this intriguing topic.
The Average Cigarette Burn Time: A Baseline
On average, a standard, commercially produced cigarette will burn for approximately 5 to 12 minutes. This range represents a significant variation, highlighting that burn time isn’t a constant. This average is based on extensive observations and, anecdotally, from our own experiences observing people smoking. However, this is just a starting point. To truly understand cigarette burn times, we need to examine the individual factors that contribute to these differences.
- Typical Range: 5-12 minutes
- Important Note: This is an average, and individual experiences can vary significantly.
Key Factors Affecting Cigarette Burn Time
Numerous factors influence how quickly a cigarette burns. These factors can be broadly categorized into cigarette construction, smoking habits, and environmental conditions. Understanding these categories provides a framework for predicting burn times and appreciating the complexity of the process.
Cigarette Construction and Composition
The materials and design of the cigarette itself play a crucial role. These factors are controlled by manufacturers and directly impact the burning characteristics of the product.
- Tobacco Type and Density: The type of tobacco used (e.g., Virginia, Burley, Oriental) and how tightly it’s packed significantly affect burn rate. Denser tobacco burns slower.
- Paper Thickness and Porosity: Thicker paper and paper with lower porosity (fewer air holes) tend to burn slower. The paper acts as a wick, supporting the combustion of the tobacco.
- Additives: Some additives are designed to influence burn rate, often to ensure a consistent and even burn.
- Cigarette Length and Diameter: Naturally, a longer or thicker cigarette will generally burn for a longer period.
Smoking Habits: How You Smoke Matters
The smoker’s behavior has a profound impact on burn time. Puffing frequency, draw strength, and even how the cigarette is held can all contribute.
- Puff Frequency: More frequent puffs introduce more oxygen, accelerating the burning process.
- Puff Strength: Stronger draws pull more heat and oxygen through the cigarette, leading to a faster burn.
- Inhalation Technique: The way a smoker inhales (e.g., direct lung inhale vs. mouth inhale) can indirectly affect burn time by influencing puff frequency and strength.
- Holding the Cigarette: Holding the cigarette in a way that exposes it to more airflow (e.g., outside a window on a windy day) will increase the burn rate.
Environmental Conditions: The External Influence
External factors, particularly airflow and humidity, can significantly alter how a cigarette burns.
- Airflow (Wind): Wind provides a constant supply of oxygen, dramatically increasing the burn rate. A cigarette smoked outdoors on a windy day will burn much faster than one smoked indoors.
- Humidity: High humidity can slow down the burn rate, as the moisture in the air inhibits combustion. Conversely, dry air can accelerate burning.
- Temperature: While less significant than airflow or humidity, extreme temperatures can also have a minor impact on burn time.
The Science Behind the Burn: Combustion and Nicotine Delivery
The burning of a cigarette is a complex chemical process involving combustion, pyrolysis, and distillation. Understanding these processes provides a deeper appreciation for the factors influencing burn time and nicotine delivery.
- Combustion: The burning of the tobacco and paper releases heat and various chemical compounds.
- Pyrolysis: The heat from combustion causes the tobacco to decompose, releasing additional volatile compounds.
- Distillation: The heat also vaporizes nicotine and other substances, which are then inhaled by the smoker.
The rate at which these processes occur is directly influenced by the factors discussed earlier. A faster burn rate means a quicker release of nicotine, while a slower burn rate allows for a more gradual delivery. However, it’s important to note that the relationship between burn time and nicotine delivery isn’t always linear. Other factors, such as the type of tobacco and the filter design, also play a significant role.
Cigarette Filters: Design, Materials and Impact on Burn Time
Cigarette filters are an integral part of the cigarette design, primarily intended to reduce the amount of tar and nicotine inhaled by the smoker. They are typically made of cellulose acetate fibers, a type of plastic that can trap some of the particulate matter in smoke. The design, materials, and presence of ventilation holes in the filter can all have an impact on the cigarette’s burn time.
- Filter Density: A denser filter might slightly restrict airflow, potentially leading to a slower burn time. However, this effect is generally minimal.
- Ventilation Holes: Many cigarettes have ventilation holes in the filter to dilute the smoke with air. These holes can increase the overall airflow around the burning tobacco, potentially leading to a faster burn rate, especially if the smoker doesn’t cover the holes with their fingers or lips.
- Filter Material: The material of the filter itself doesn’t directly affect the burn time of the tobacco. Its primary role is to filter out particles from the smoke.
Comparing Cigarette Brands: Burn Time Variations
Different cigarette brands utilize different tobacco blends, paper types, and filter designs, leading to variations in burn time. While specific burn times for each brand are not publicly available, some generalizations can be made based on observable characteristics.
- American Spirit: Often noted for their tightly packed tobacco and lack of additives, American Spirit cigarettes tend to burn longer than many other brands.
- Marlboro: A popular brand with a wide range of varieties, Marlboro cigarettes generally have a moderate burn time.
- Camel: Known for its distinctive blend of Turkish and Virginia tobaccos, Camel cigarettes tend to burn at a rate similar to Marlboro.
- Generic Brands: Budget-friendly generic brands often use lower-quality tobacco and less dense packing, resulting in a faster burn time.
It’s important to remember that these are general observations, and individual experiences may vary. Furthermore, manufacturers may change their formulations over time, affecting burn times.
The Impact of Burn Time on Smoking Behavior and Nicotine Intake
The burn time of a cigarette directly influences smoking behavior and nicotine intake. Smokers often unconsciously adjust their puffing habits to achieve a desired level of nicotine satisfaction. A cigarette that burns too quickly may lead to more frequent puffs, while one that burns too slowly may result in a less satisfying experience.
- Nicotine Regulation: Smokers often regulate their nicotine intake by adjusting their smoking behavior based on how quickly the cigarette burns.
- Satisfaction Levels: A cigarette that burns at a comfortable pace is more likely to provide a satisfying smoking experience.
Understanding the relationship between burn time and nicotine intake can be valuable for smokers who are trying to quit or reduce their consumption. By choosing cigarettes with a longer burn time or by consciously slowing down their puffing habits, smokers may be able to better control their nicotine intake.
The Health Implications of Cigarette Burn Time
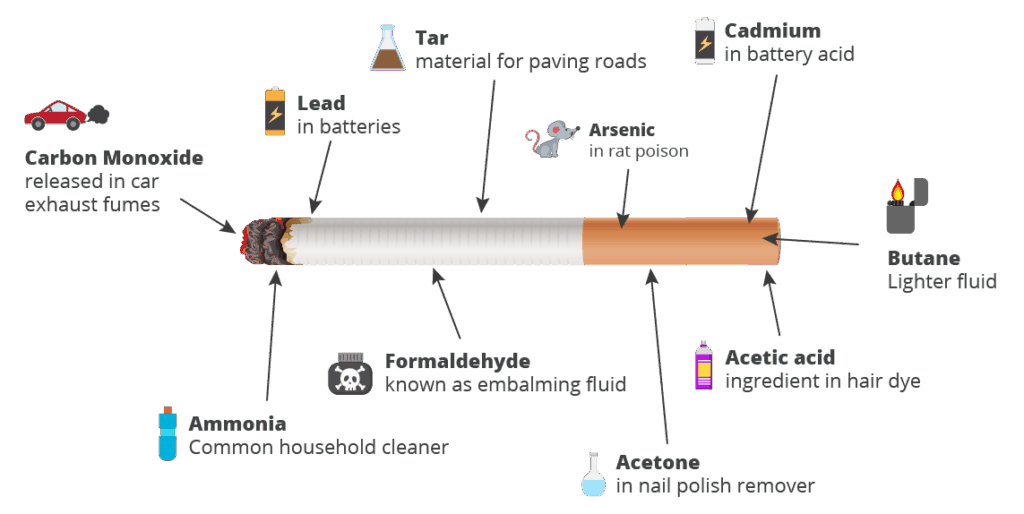
While the primary health risks associated with smoking stem from the harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke, burn time can indirectly influence these risks. A faster burn rate may lead to the inhalation of a greater volume of smoke over a shorter period, potentially increasing exposure to harmful substances. Also, a study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute indicated that individuals who smoke cigarettes that burn faster tend to inhale more deeply, increasing their risk of respiratory illnesses.
- Exposure to Harmful Chemicals: Faster burn rates may lead to increased exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Inhalation Depth: Smokers of faster-burning cigarettes may inhale more deeply, increasing their risk of respiratory illnesses.
It’s crucial to emphasize that there is no safe level of smoking. However, understanding the relationship between burn time and health risks can help smokers make more informed decisions about their smoking habits.
Alternatives to Traditional Cigarettes: E-Cigarettes and Burn Time
E-cigarettes, also known as vapes, offer an alternative to traditional cigarettes that eliminates the burning process altogether. Instead of burning tobacco, e-cigarettes heat a liquid containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals, producing an aerosol that is inhaled by the user. This fundamental difference has significant implications for nicotine delivery, health risks, and the overall smoking experience.
- No Combustion: E-cigarettes do not involve combustion, eliminating the production of harmful smoke.
- Variable Nicotine Delivery: E-cigarettes allow users to control the nicotine concentration and puffing patterns, offering a more customizable nicotine delivery experience.
While e-cigarettes are often marketed as a safer alternative to traditional cigarettes, it’s important to note that they are not without risks. The long-term health effects of e-cigarette use are still being studied, and concerns remain about the potential for nicotine addiction and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Expert Insights: Tips for Managing Cigarette Burn Time
Based on our experience and observations, here are some practical tips for managing cigarette burn time:
- Choose Cigarettes with Tightly Packed Tobacco: Cigarettes with denser tobacco tend to burn slower.
- Avoid Smoking in Windy Conditions: Wind significantly accelerates burn rate.
- Puff Less Frequently: Reducing puff frequency will slow down the burning process.
- Store Cigarettes Properly: Keep cigarettes in a cool, dry place to prevent them from drying out and burning too quickly.
These tips can help smokers gain more control over their smoking experience and potentially reduce their nicotine intake. However, the most effective way to manage the health risks associated with smoking is to quit altogether.
How Long Does a Cigarette Last? More Than Just a Number
As we’ve explored, the answer to how long does a cigarette burns for is far from simple. It’s a dynamic process influenced by a complex interplay of factors, from the cigarette’s construction to the smoker’s habits and the surrounding environment. Understanding these factors provides valuable insights into smoking behavior, nicotine delivery, and the potential health consequences.
Ultimately, whether you’re a smoker seeking to understand your habit better or simply curious about the world around you, we hope this comprehensive guide has provided a thorough and informative exploration of this intriguing topic. If you are considering quitting, numerous resources are available to support you. Talk to your doctor or visit the CDC website for more information.
