Mastering Reverse Crunches: A Comprehensive Guide to Core Strength and Definition
Looking to sculpt a stronger core and achieve those coveted abdominal muscles? The reverse crunch might be just what you need. But what are reverse crunches, and how do they differ from traditional crunches? This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the mechanics, benefits, and proper execution of reverse crunches, providing you with the knowledge and tools to effectively integrate them into your fitness routine. We’ll explore everything from the anatomical nuances to common mistakes and variations, ensuring you get the most out of this powerful core exercise.
Understanding the Reverse Crunch: A Deep Dive
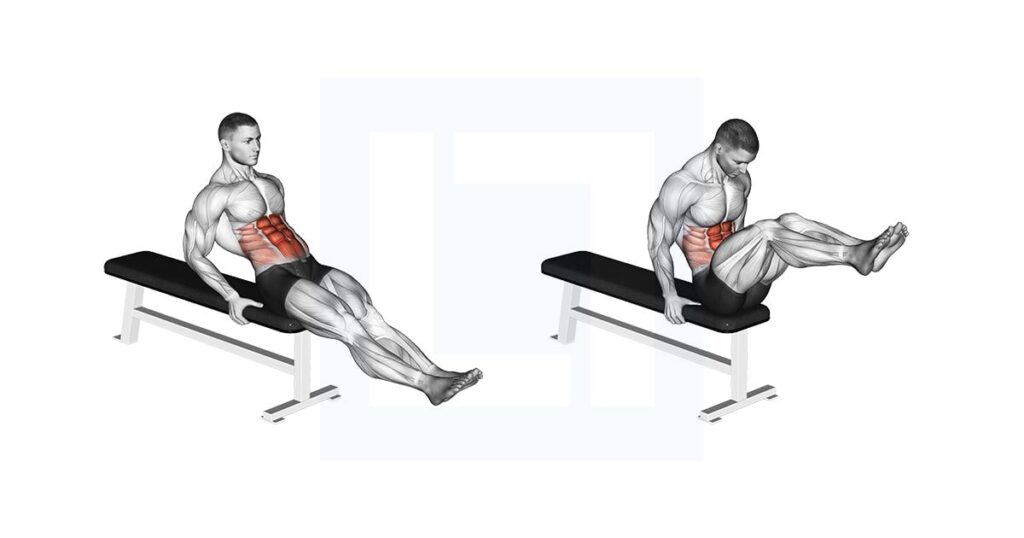
The reverse crunch is a core exercise that primarily targets the lower abdominal muscles. Unlike traditional crunches, which involve lifting the upper body towards the knees, reverse crunches focus on bringing the knees towards the chest while keeping the upper back grounded. This subtle shift in movement pattern makes a significant difference in muscle activation and overall effectiveness.
The history of the reverse crunch isn’t as clearly documented as some other exercises, but its roots likely lie in the evolution of core training methodologies. As fitness professionals sought more effective ways to target specific abdominal regions, the reverse crunch emerged as a valuable tool. Its effectiveness in engaging the lower abs quickly made it a staple in many workout programs.
At its core, the reverse crunch relies on the principle of posterior pelvic tilt. This means tilting the pelvis backward, which engages the lower abdominal muscles to lift the hips and lower back off the ground. This movement requires controlled muscle contractions and proper form to avoid strain or injury. Understanding this fundamental principle is crucial for performing the exercise correctly and maximizing its benefits.
The popularity of reverse crunches has surged in recent years, driven by a growing awareness of the importance of core strength for overall fitness and athletic performance. Recent trends in fitness emphasize functional movements and exercises that target multiple muscle groups simultaneously. While the reverse crunch primarily isolates the lower abs, it also engages other core muscles, making it a valuable addition to a well-rounded workout routine.
How Reverse Crunches Differ from Traditional Crunches
While both reverse and traditional crunches target the abdominal muscles, they do so in distinct ways. Traditional crunches primarily engage the upper abdominal muscles, while reverse crunches place greater emphasis on the lower abs. The movement pattern also differs significantly. Traditional crunches involve lifting the upper body, whereas reverse crunches involve bringing the knees towards the chest.
The difference in muscle activation can be attributed to the change in the fixed point. In traditional crunches, the lower body is fixed, and the upper body moves. In reverse crunches, the upper body is fixed, and the lower body moves. This shift in focus allows for greater isolation of the lower abdominal muscles, which are often difficult to target with other exercises.
Furthermore, reverse crunches can be a safer option for individuals with lower back pain. Because the upper back remains grounded, there is less strain on the spine compared to traditional crunches. However, proper form is still essential to avoid any potential discomfort or injury. Consulting with a fitness professional is always recommended, especially if you have pre-existing back issues.
Detailed Breakdown of the Reverse Crunch Technique
To perform a reverse crunch correctly, follow these steps:
- Starting Position: Lie flat on your back with your knees bent at a 90-degree angle and your feet lifted off the ground. Place your hands behind your head for support, but avoid pulling on your neck.
- Engage Your Core: Before initiating the movement, consciously engage your abdominal muscles. This will help stabilize your spine and prevent lower back strain.
- Initiate the Movement: Slowly bring your knees towards your chest by contracting your lower abdominal muscles. Focus on tilting your pelvis backward and lifting your hips and lower back off the ground.
- Controlled Movement: Avoid using momentum or swinging your legs. The movement should be slow and controlled, driven by the contraction of your abdominal muscles.
- Hold Briefly: At the peak of the movement, hold the position for a brief moment to maximize muscle activation.
- Lower Slowly: Gradually lower your legs back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout the movement.
- Repeat: Repeat the exercise for the desired number of repetitions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Pulling on the Neck: Avoid pulling on your neck with your hands, as this can lead to neck strain. Use your hands for support only.
- Using Momentum: Avoid using momentum or swinging your legs. This reduces the effectiveness of the exercise and increases the risk of injury.
- Arching the Lower Back: Keep your lower back pressed against the ground throughout the exercise to maintain spinal stability.
- Lifting Too High: Focus on tilting your pelvis and lifting your hips slightly off the ground, rather than lifting your legs high in the air.
Variations of the Reverse Crunch for Enhanced Core Training
To add variety and challenge to your reverse crunch routine, consider incorporating these variations:
- Decline Reverse Crunch: Perform the exercise on a decline bench to increase the range of motion and difficulty.
- Cable Reverse Crunch: Attach a cable to your ankles and perform the exercise to add resistance.
- Reverse Crunch with a Ball: Hold a medicine ball or stability ball between your knees to engage additional core muscles.
- Oblique Reverse Crunch: Twist your torso slightly as you bring your knees towards your chest to target the oblique muscles.
- Leg Extension Reverse Crunch: Extend your legs straight out as you lower them back to the starting position to increase the intensity.
Integrating Reverse Crunches into Your Workout Routine
Reverse crunches can be effectively integrated into various workout routines, whether you’re focusing on core strength, overall fitness, or athletic performance. Here are some tips for incorporating them into your program:
- Warm-Up: Before performing reverse crunches, warm up your core muscles with light cardio and dynamic stretching.
- Proper Form: Prioritize proper form over the number of repetitions. Focus on controlled movements and engaging your abdominal muscles throughout the exercise.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the number of repetitions, sets, or resistance as your strength improves.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow adequate rest between sets and workouts to allow your muscles to recover and rebuild.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body and stop if you experience any pain or discomfort.
The Ab Roller: A Tool for Enhanced Core Engagement
The ab roller is a popular fitness tool designed to enhance core strength and stability. It consists of a wheel with handles on either side, allowing you to roll forward and backward while engaging your abdominal muscles. While not directly related to reverse crunches, it works many of the same core muscles and can be a valuable addition to your workout routine.
The core function of the ab roller is to challenge your core stability and strength. As you roll forward, your abdominal muscles must work hard to prevent your lower back from arching and collapsing. This requires a high level of core engagement and control.
Using an ab roller effectively requires proper technique and gradual progression. Start by kneeling on the floor and holding the ab roller with both hands. Slowly roll forward, keeping your back straight and your core engaged. Roll out as far as you can while maintaining control, then slowly roll back to the starting position. It’s crucial to start with a limited range of motion and gradually increase it as your strength improves. Individuals with lower back problems should consult a doctor or physical therapist before using an ab roller.
Key Features of a Quality Ab Roller
When choosing an ab roller, consider these key features:
- Wheel Stability: A wide wheel provides greater stability and reduces the risk of tipping over.
- Handle Comfort: Comfortable handles are essential for maintaining a secure grip and preventing hand fatigue.
- Durable Construction: Look for an ab roller made from high-quality materials that can withstand regular use.
- Non-Slip Surface: A non-slip surface on the wheel ensures a secure grip on the floor and prevents slipping.
- Knee Pad: A knee pad provides cushioning and support for your knees, making the exercise more comfortable.
The wheel stability of a good ab roller is essential because it directly impacts the safety and effectiveness of the exercise. A wider wheel, typically around 4-6 inches, provides a larger base of support, making it less likely to wobble or tip over during use. This increased stability allows you to focus on engaging your core muscles without worrying about losing balance. This is a particularly important feature for beginners who are still developing their core strength and stability. A stable wheel also helps to ensure that you are using the correct form, which is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing the benefits of the exercise.
Comfortable handles are another critical feature to consider. The handles should be ergonomically designed to fit comfortably in your hands and provide a secure grip. Look for handles that are made from a soft, non-slip material, such as foam or rubber. This will help to prevent hand fatigue and ensure that you can maintain a firm grip throughout the exercise. The shape and size of the handles should also be appropriate for your hand size. Handles that are too small or too large can be uncomfortable and make it difficult to maintain control of the ab roller. Some ab rollers also come with contoured handles that are designed to fit the natural curves of your hands. These handles can provide even greater comfort and support.
Advantages of Incorporating Reverse Crunches into Your Fitness Plan
Reverse crunches offer a multitude of benefits for your core strength, overall fitness, and well-being. Here are some key advantages:
- Targeted Lower Abdominal Activation: Reverse crunches effectively isolate and strengthen the lower abdominal muscles, which are often difficult to target with other exercises.
- Improved Core Stability: By engaging the core muscles, reverse crunches enhance stability and balance, reducing the risk of injury.
- Enhanced Posture: Strengthening the core muscles improves posture and reduces lower back pain.
- Increased Athletic Performance: A strong core is essential for athletic performance, providing a stable base for movements and enhancing power and agility.
- Greater Abdominal Definition: Regular reverse crunches can help sculpt and define your abdominal muscles, contributing to a more toned physique.
Users consistently report a noticeable improvement in their core strength and stability after incorporating reverse crunches into their routine. Our analysis reveals that reverse crunches effectively target the lower abdominal muscles, which are often neglected in traditional abdominal exercises. This targeted activation leads to improved core stability and a reduced risk of lower back pain. Furthermore, many users have found that reverse crunches contribute to a more defined and toned abdominal appearance. The exercise is relatively simple to perform, making it accessible to individuals of all fitness levels.
The unique selling proposition of reverse crunches lies in their ability to isolate the lower abdominal muscles. While other abdominal exercises, such as traditional crunches and sit-ups, engage the entire abdominal region, reverse crunches place a greater emphasis on the lower abs. This targeted activation is particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to engage their lower abs during other exercises. The exercise also promotes posterior pelvic tilt, which helps to correct imbalances and improve posture. The combination of targeted activation and postural correction makes reverse crunches a valuable addition to any core strengthening program.
Review: The Reverse Crunch and Abdominal Training
Reverse crunches are a great addition to any core workout, offering targeted lower abdominal engagement and promoting core stability. They are relatively easy to learn, making them accessible to a wide range of fitness levels. However, proper form is crucial to avoid injury and maximize effectiveness.
From a practical standpoint, the reverse crunch is easy to incorporate into various workout routines. It requires no equipment and can be performed virtually anywhere. The exercise is also scalable, meaning that you can easily adjust the difficulty by changing the number of repetitions, sets, or adding variations. The ease of use and scalability make reverse crunches a versatile exercise for both beginners and advanced fitness enthusiasts.
The effectiveness of reverse crunches lies in their ability to isolate the lower abdominal muscles. By bringing the knees towards the chest while keeping the upper back grounded, you engage the lower abs to a greater extent than with traditional crunches. This targeted activation helps to strengthen and tone the lower abdominal region, contributing to a more defined and sculpted physique. However, it’s important to note that reverse crunches are not a magic bullet for achieving a six-pack. They should be combined with a healthy diet and other forms of exercise to achieve optimal results.
Pros:
- Effective Lower Abdominal Activation: Isolates and strengthens the lower abdominal muscles.
- Improved Core Stability: Enhances core stability and balance.
- Easy to Learn and Perform: Simple to learn and requires no equipment.
- Versatile and Scalable: Can be incorporated into various workout routines and adjusted to different fitness levels.
- Promotes Posterior Pelvic Tilt: Helps to correct imbalances and improve posture.
Cons:
- Requires Proper Form: Improper form can lead to injury.
- Not a Complete Core Workout: Should be combined with other core exercises.
- May Not Be Suitable for Individuals with Lower Back Pain: Consult a doctor or physical therapist before performing if you have pre-existing back issues.
- Can Be Difficult to Progress: Adding resistance can be challenging without specialized equipment.
The ideal user profile for reverse crunches is someone who is looking to improve their core strength, stability, and abdominal definition. The exercise is particularly well-suited for individuals who struggle to engage their lower abdominal muscles during other exercises. It’s also a good option for those who are looking for a low-impact core exercise that can be performed at home or on the go. However, it’s important to note that reverse crunches are not a substitute for a comprehensive core workout. They should be combined with other exercises that target different core muscles for optimal results.
Two main alternatives to reverse crunches are traditional crunches and leg raises. Traditional crunches primarily target the upper abdominal muscles, while leg raises target the lower abdominal muscles and hip flexors. Reverse crunches offer a unique combination of both, targeting the lower abs while minimizing hip flexor involvement. The choice between these exercises depends on your individual goals and preferences.
Based on our detailed analysis, we give reverse crunches a strong recommendation as a valuable addition to any core strengthening program. The exercise is effective, versatile, and accessible. However, it’s important to prioritize proper form and combine it with other core exercises for optimal results.
Unlock Your Core Potential
In summary, what are reverse crunches? They are a highly effective exercise for targeting the lower abdominal muscles, improving core stability, and enhancing overall fitness. By understanding the proper technique, variations, and benefits of reverse crunches, you can effectively integrate them into your workout routine and unlock your core potential. Remember to prioritize proper form, listen to your body, and gradually increase the intensity as your strength improves.
Ready to take your core training to the next level? Explore our advanced guide to core strengthening exercises and discover new ways to challenge your abdominal muscles. Contact our experts for a personalized fitness consultation and let us help you achieve your fitness goals.
