Quarantine Unveiled: Weighing the Pros and Cons of Isolation
In an interconnected world, the concept of quarantine has become increasingly relevant, particularly in the face of global health crises. The decision to implement quarantine measures is a complex one, laden with ethical, social, and economic considerations. This comprehensive guide delves into the advantages and disadvantages of quarantine, providing a balanced perspective to help you understand its multifaceted nature and impacts on individual lives and society as a whole. We aim to offer a deeper understanding of the strategies and consequences of quarantine, drawing on expert insights and real-world examples.
Understanding the Purpose and Principles of Quarantine
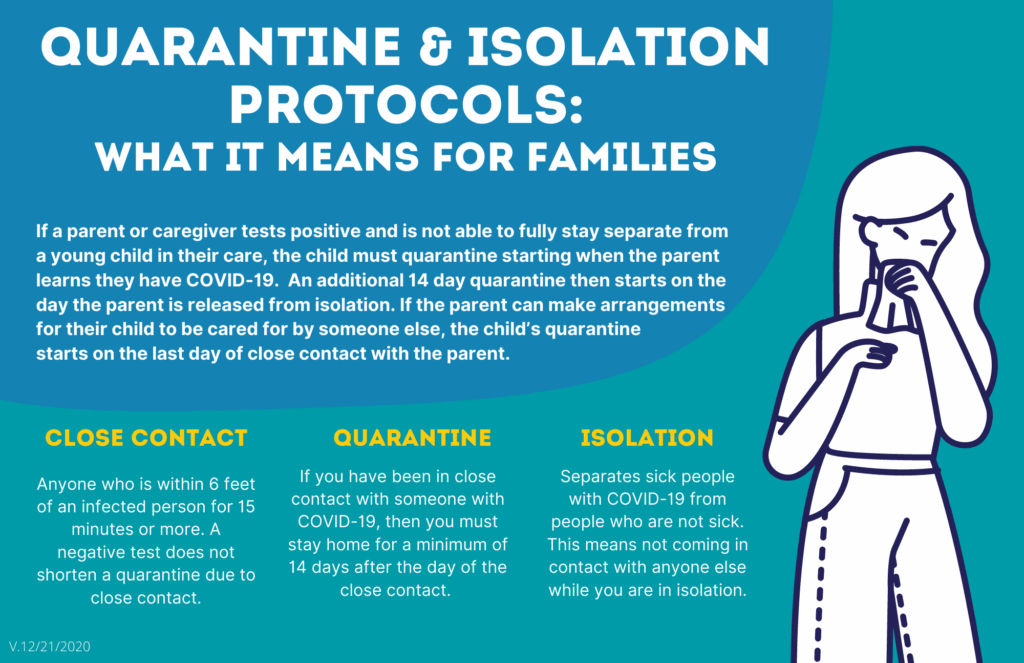
Quarantine, at its core, is a public health strategy designed to limit the spread of contagious diseases. It involves the separation and restriction of movement of individuals who have been exposed to an infectious agent but are not yet showing symptoms. This differs from isolation, which applies to individuals who are already ill. The underlying principle is to break the chain of transmission by preventing contact between potentially infected individuals and the healthy population.
The effectiveness of quarantine depends on several factors, including the characteristics of the disease (e.g., incubation period, transmissibility), the compliance of the population, and the availability of resources for monitoring and support. Quarantine measures can range from voluntary self-quarantine to mandatory government-imposed restrictions, each with its own set of challenges and ethical implications. Understanding these nuances is crucial for evaluating the overall impact of quarantine.
The Advantages of Implementing Quarantine Measures
Quarantine, when implemented effectively, offers several key advantages in controlling and mitigating the spread of infectious diseases. These benefits extend to both individual and societal levels.
Slowing Disease Transmission
The most significant advantage of quarantine is its ability to slow down the rate of disease transmission. By restricting the movement of potentially infected individuals, quarantine reduces the number of contacts they have with others, thereby limiting opportunities for the virus or bacteria to spread. This is particularly crucial in the early stages of an outbreak when the full extent of the spread is not yet known. Mathematical models consistently show that even modest reductions in transmission rates can have a significant impact on the overall course of an epidemic.
Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Quarantine provides a vital layer of protection for vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, individuals with underlying health conditions, and those with weakened immune systems. These groups are often at higher risk of developing severe complications from infectious diseases. By reducing the overall spread of the disease, quarantine minimizes the likelihood that these vulnerable individuals will be exposed, thereby safeguarding their health and well-being. Public health data consistently demonstrates the effectiveness of quarantine in shielding high-risk groups.
Preventing Healthcare System Overload
During a pandemic, healthcare systems can quickly become overwhelmed with a surge in patients requiring medical care. Quarantine can help to flatten the curve, meaning it spreads out the number of cases over a longer period, preventing hospitals and clinics from being overloaded. This allows healthcare providers to provide better care to those who need it most and reduces the risk of shortages in essential medical supplies and equipment. The experience during the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the critical role of quarantine in preserving healthcare capacity.
Buying Time for Medical Advancements
Quarantine buys valuable time for researchers and healthcare professionals to develop and implement effective treatments and vaccines. During the initial stages of an outbreak, when little is known about the disease, quarantine can help to slow the spread while scientists work to understand the virus or bacteria and develop strategies to combat it. This was evident during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, where quarantine measures allowed researchers to rapidly develop vaccines and antiviral therapies. The development of effective treatments can significantly reduce the severity and mortality of the disease.
Enhancing Public Awareness and Preparedness
The implementation of quarantine measures can raise public awareness about the importance of hygiene, social distancing, and other preventive measures. It also encourages individuals to take personal responsibility for protecting themselves and others from infection. Furthermore, the experience of going through a quarantine can help communities to better prepare for future outbreaks by identifying gaps in their preparedness plans and strengthening their public health infrastructure. For example, communities might invest in improved testing capacity or develop more effective communication strategies.
The Disadvantages and Challenges of Quarantine
While quarantine offers significant benefits, it also presents a number of disadvantages and challenges that must be carefully considered. These drawbacks can affect individuals, communities, and the economy.
Economic Disruptions
One of the most significant disadvantages of quarantine is its potential to cause widespread economic disruption. When individuals are unable to work, businesses may be forced to close, leading to job losses and reduced economic activity. Supply chains can also be disrupted, leading to shortages of essential goods and services. The economic impact of quarantine can be particularly severe for small businesses and low-income workers who may not have the resources to weather prolonged periods of inactivity. Governments often need to provide financial assistance to mitigate the economic consequences of quarantine, which can strain public resources.
Psychological and Social Impacts
Quarantine can have significant psychological and social impacts on individuals. Isolation and loneliness can lead to increased stress, anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. Individuals may also experience feelings of fear, uncertainty, and stigma. The social isolation associated with quarantine can also disrupt social networks and support systems, leading to feelings of alienation and disconnection. Children and adolescents may be particularly vulnerable to the psychological effects of quarantine, as they may miss out on important social interactions and educational opportunities. Studies have shown a correlation between prolonged quarantine and increased rates of mental health disorders.
Ethical and Legal Concerns
The implementation of quarantine raises a number of ethical and legal concerns. Mandatory quarantine measures can infringe on individual liberties, such as the right to freedom of movement and association. It is essential to ensure that quarantine measures are proportionate to the risk posed by the disease and that they are implemented in a fair and equitable manner. Governments must also provide adequate support and resources to individuals who are subject to quarantine, including access to food, shelter, medical care, and mental health services. Balancing public health interests with individual rights is a complex ethical challenge.
Logistical and Practical Difficulties
Implementing quarantine effectively can be logistically challenging. It requires significant resources for monitoring compliance, providing support to quarantined individuals, and ensuring that essential services are maintained. Enforcing quarantine measures can be difficult, particularly if there is a lack of public trust or cooperation. It is also important to consider the needs of vulnerable populations, such as individuals with disabilities or language barriers, who may require additional support. Effective communication and coordination between government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations are essential for successful quarantine implementation.
Potential for Social Unrest
In some cases, the implementation of quarantine can lead to social unrest and civil disobedience. If people feel that quarantine measures are unfair, excessive, or poorly implemented, they may be more likely to resist or protest. This can undermine the effectiveness of quarantine and create additional challenges for public health authorities. It is crucial to engage with communities and address their concerns to build trust and ensure cooperation. Transparency and accountability are essential for maintaining public confidence in quarantine measures.
Navigating the Challenges: Strategies for Effective Quarantine
To maximize the benefits and minimize the drawbacks of quarantine, it is essential to implement it strategically and thoughtfully. Several key strategies can enhance the effectiveness and reduce the negative impacts of quarantine.
- Clear and Transparent Communication: Public health authorities must communicate clearly and transparently about the rationale for quarantine, the measures being implemented, and the support available to quarantined individuals. This helps to build trust and encourages compliance.
- Targeted and Proportionate Measures: Quarantine measures should be targeted to specific populations and tailored to the specific characteristics of the disease. Overly broad or restrictive measures can be counterproductive and can lead to unnecessary economic and social disruption.
- Adequate Support and Resources: Governments must provide adequate support and resources to individuals who are subject to quarantine, including access to food, shelter, medical care, mental health services, and financial assistance.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with communities and addressing their concerns is essential for building trust and ensuring cooperation. Public health authorities should work with community leaders and organizations to develop culturally appropriate and effective quarantine strategies.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Quarantine measures should be continuously monitored and evaluated to assess their effectiveness and identify any unintended consequences. This allows for adjustments to be made as needed to optimize the impact of quarantine.
The Future of Quarantine in a Globalized World
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the risk of infectious disease outbreaks will likely continue to grow. Quarantine will remain an important tool for controlling and mitigating the spread of these diseases. However, it is essential to learn from past experiences and to develop more effective and equitable quarantine strategies. Investing in public health infrastructure, strengthening international collaboration, and promoting public awareness are crucial steps for preparing for future pandemics. By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of quarantine and implementing it strategically, we can protect public health while minimizing the negative impacts on individuals and society.
Weighing the Options: Informed Decisions About Quarantine
The decision to implement quarantine is a complex one with significant implications for public health, the economy, and individual liberties. While quarantine offers several advantages in controlling and mitigating the spread of infectious diseases, it also presents a number of challenges and drawbacks. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of quarantine, and by implementing it strategically and thoughtfully, we can maximize its benefits while minimizing its negative impacts. The experiences from recent years show the value of ongoing research and improved communication strategies to navigate these difficult decisions.
