Understanding Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (CSID): A Comprehensive Guide
Are you struggling with digestive issues after eating sugary foods or starches? Do you suspect a problem beyond typical food sensitivities? You might be searching for answers about Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (CSID), a genetic condition affecting your ability to digest certain sugars. This comprehensive guide delves deep into CSID, offering a detailed understanding of the condition, its symptoms, diagnosis, management, and the latest advancements in research. We aim to provide you with the most up-to-date and reliable information, empowering you to navigate life with CSID with confidence. This resource is designed to be more than just an overview; it’s a roadmap to understanding and managing CSID effectively. We’ll explore the nuances of this condition, providing insights often overlooked in standard medical literature.
What is Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (CSID)?
Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency, also known as GSID, is an inherited disorder that affects the small intestine’s ability to digest sucrose (table sugar) and maltose (a sugar found in starches). This deficiency stems from a mutation in the SI gene, which provides instructions for making the sucrase-isomaltase enzyme. This enzyme is crucial for breaking down sucrose and maltose into simpler sugars that the body can absorb. When this enzyme is deficient or absent, undigested sugars accumulate in the gut, leading to a range of gastrointestinal symptoms. The severity of CSID can vary greatly among individuals, with some experiencing mild discomfort and others facing significant challenges in managing their diet and overall health. The prevalence of CSID varies depending on ethnicity, with a higher incidence observed in individuals of Greenlandic Inuit descent. While CSID is a lifelong condition, proper management and dietary modifications can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
Historically, CSID was often misdiagnosed or overlooked, leading to prolonged periods of discomfort and uncertainty for patients. However, advancements in genetic testing and diagnostic procedures have improved the accuracy and speed of diagnosis. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the underlying mechanisms of CSID and to develop more effective treatment strategies. Understanding the complexities of CSID is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals to ensure timely diagnosis, appropriate management, and improved outcomes.
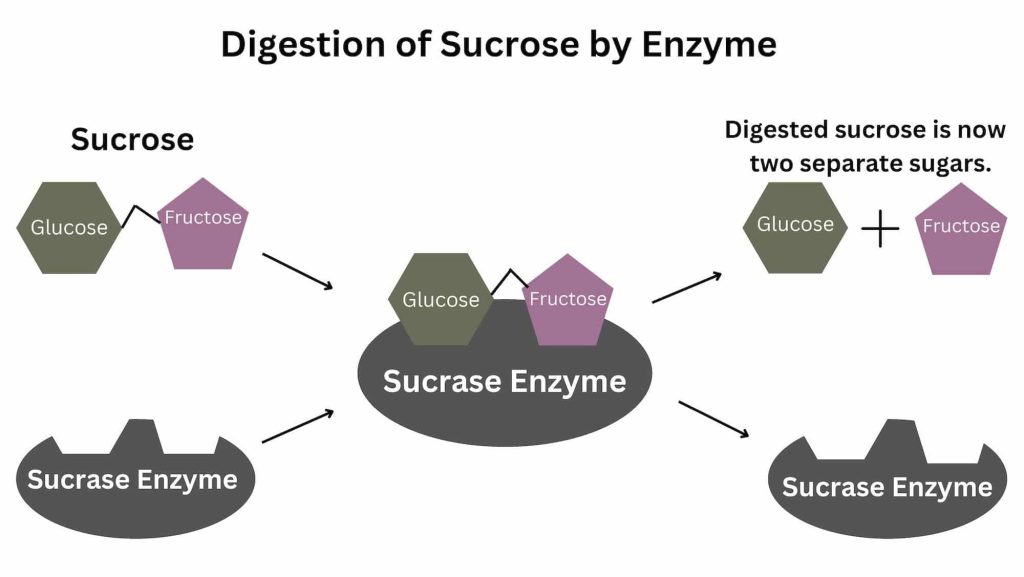
Understanding Sucraid®: An Enzyme Replacement Therapy
For individuals with CSID, managing the condition often involves dietary modifications and, in some cases, enzyme replacement therapy. Sucraid® is a prescription medication that contains the sucrase enzyme, which is deficient or absent in people with CSID. This enzyme helps break down sucrose into glucose and fructose, which can then be absorbed by the body. Sucraid® is not a cure for CSID, but it can significantly reduce the symptoms associated with sucrose ingestion, allowing individuals to enjoy a more varied diet and improve their overall quality of life. It is important to note that Sucraid® does not address maltose intolerance, which is another component of CSID. Therefore, dietary modifications to limit maltose intake are still necessary. Sucraid® is typically taken with meals that contain sucrose, and the dosage is determined by a healthcare professional based on individual needs and tolerance levels. Regular monitoring and communication with a healthcare provider are essential to ensure the effectiveness and safety of Sucraid® therapy.
Sucraid® has been a game-changer for many individuals with CSID, providing them with a greater sense of freedom and control over their dietary choices. However, it is crucial to understand that Sucraid® is not a substitute for a well-planned and managed diet. It is a tool that, when used in conjunction with dietary modifications, can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Key Features of Sucraid® for Managing CSID
Sucraid® offers several key features that make it a valuable tool in managing Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency. Understanding these features can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment.
- Enzyme Replacement: Sucraid® provides a direct replacement for the deficient sucrase enzyme, enabling the digestion of sucrose. This is the core function of the medication, addressing the root cause of sucrose intolerance in CSID.
- Targeted Action: The enzyme in Sucraid® specifically targets sucrose, breaking it down into simpler sugars that the body can absorb. This targeted action minimizes the risk of side effects associated with broader digestive enzyme supplements.
- Liquid Formulation: Sucraid® is available in a liquid formulation, making it easy to administer, especially to children and infants with CSID. The liquid form also allows for flexible dosing, as it can be easily measured and adjusted to meet individual needs.
- Mealtime Administration: Sucraid® is designed to be taken with meals containing sucrose, ensuring that the enzyme is present when it is needed most. This timing optimizes the digestion of sucrose and reduces the likelihood of symptoms.
- Improved Dietary Tolerance: By aiding in the digestion of sucrose, Sucraid® can improve an individual’s tolerance to a wider range of foods, enhancing their dietary options and quality of life. This can lead to better nutritional intake and overall health.
- Reduced Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Sucraid® can significantly reduce the gastrointestinal symptoms associated with sucrose intolerance, such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and gas. This can lead to greater comfort and improved daily functioning.
- Clinically Proven Efficacy: Sucraid® has been studied in clinical trials and has demonstrated efficacy in improving sucrose digestion and reducing symptoms in individuals with CSID. This evidence supports its use as a valuable treatment option.
Advantages, Benefits, and Real-World Value of Managing CSID
Managing Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency effectively offers a multitude of advantages, benefits, and real-world value for individuals living with this condition. By understanding these benefits, patients and their families can be motivated to adhere to dietary recommendations and treatment plans, leading to improved health and well-being. The core advantage lies in mitigating the debilitating symptoms that can significantly impact daily life.
- Symptom Relief: Effective management of CSID leads to a significant reduction in gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and gas. This relief can dramatically improve comfort and overall quality of life.
- Improved Nutritional Status: By carefully managing their diet and, when appropriate, using enzyme replacement therapy, individuals with CSID can improve their nutritional intake and avoid deficiencies. This is particularly important for children, as proper nutrition is essential for growth and development.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Undigested sugars can lead to fatigue and low energy levels. Effective management of CSID can improve energy levels, allowing individuals to participate more fully in daily activities.
- Greater Dietary Freedom: While dietary modifications are necessary, effective management can allow for a more varied and enjoyable diet. This can reduce the sense of restriction and improve overall satisfaction with food.
- Improved Social Interactions: Gastrointestinal symptoms can be embarrassing and isolating. By managing these symptoms, individuals with CSID can feel more confident and comfortable in social situations.
- Better School/Work Performance: Reduced symptoms and improved energy levels can lead to better concentration and performance in school or at work.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Proactive management of CSID can prevent complications and reduce the need for frequent medical visits, leading to lower healthcare costs over time.
A Comprehensive Review of Sucraid® for CSID Management
Sucraid® is a crucial tool for managing CSID, but like any medication, it has its pros and cons. This review aims to provide a balanced perspective on Sucraid®, based on available data and expert opinions.
User Experience & Usability: Sucraid® is generally easy to administer, especially in its liquid form. The need to take it with every sucrose-containing meal can be inconvenient, requiring careful planning and awareness of food ingredients. However, most users find that the benefits outweigh the inconvenience.
Performance & Effectiveness: Clinical studies and real-world experience suggest that Sucraid® is effective in reducing symptoms associated with sucrose ingestion. However, its effectiveness can vary depending on individual factors, such as the severity of CSID and adherence to dietary recommendations. Sucraid® does not address maltose intolerance, so dietary modifications are still necessary.
Pros:
- Effective Symptom Relief: Sucraid® can significantly reduce gastrointestinal symptoms associated with sucrose intolerance.
- Improved Dietary Tolerance: It allows for a more varied diet, enhancing quality of life.
- Easy Administration: The liquid formulation is easy to administer, especially to children.
- Clinically Proven: Its efficacy is supported by clinical studies.
- Targeted Action: It specifically targets sucrose digestion, minimizing the risk of side effects.
Cons/Limitations:
- Does Not Address Maltose Intolerance: Dietary modifications are still needed to manage maltose intake.
- Requires Careful Planning: It must be taken with every sucrose-containing meal, requiring careful planning.
- Potential Side Effects: Some individuals may experience side effects, such as nausea or abdominal discomfort.
- Cost: Sucraid® can be expensive, and insurance coverage may vary.
Ideal User Profile: Sucraid® is best suited for individuals with CSID who experience significant symptoms despite dietary modifications. It is particularly helpful for those who struggle to adhere to a strict sucrose-free diet or who desire a more varied diet. It is also a valuable option for children with CSID, as it can help ensure adequate nutrition and growth.
Key Alternatives: The primary alternative to Sucraid® is strict dietary management, which involves avoiding sucrose-containing foods. While this can be effective, it can also be challenging and restrictive. Other digestive enzyme supplements may offer some relief, but they are not specifically designed for CSID and may not be as effective as Sucraid®.
Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation: Sucraid® is a valuable tool for managing CSID and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. While it is not a cure and requires careful planning and monitoring, its benefits often outweigh its limitations. We recommend Sucraid® for individuals with CSID who experience significant symptoms despite dietary modifications, in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Navigating Life with CSID: Expert Guidance for Patients and Families
Living with Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding the condition, adhering to dietary recommendations, and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with CSID can lead fulfilling and healthy lives. Remember, you are not alone. Support groups and online communities can provide valuable resources and connections with others who understand the challenges of living with CSID. The future of CSID management is promising, with ongoing research exploring new and innovative treatment strategies. Share your experiences with Congenital Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency in the comments below. Together, we can raise awareness and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
